
Validation in the Outcome Standards
The National Vocational Education and Training Regulator (Outcome Standards for NVR Registered Training Organisations) Instrument 2025 (the 'Outcome Standards') refer to validation activities two distinct times:
- Once at Outcome Standard 1.3
- And secondly at Outcome Standard 1.5
However, explicit use of the term ‘validation’ is only made at Outcome Standard 1.5.
The performance indicators under Outcome Standard 1.3.2 use the term “reviewed” to articulate that an RTO must conduct an analysis of the assessment tools before they are used.
Note though, that the word “review” is part of the definition of validation contained in the Outcome Standards. From 2025, validation in the context of the legislative instrument means:
“…the review of the assessment system to ensure that:
- assessment tools are consistent with the training product and the requirements set out in this instrument; and
- assessments and assessment judgements are producing consistent outcomes.”
In the context of general use, 'to validate' something means to check, prove or confirm that thing is true and/or correct.
Outcome Standard 1.5 refers to the activities an RTO must undertake to confirm the processes and judgements made using the assessment tools, that is, an analysis of after they have been used.
This means there is now an explicit expectation that what goes into the assessment system meets requirements so that what comes out of the assessment system can meet requirements.
An RTO’s training and assessment programs must be informed by the advice and feedback received from employers and other representatives in industry to ensure students are getting up-to-date skills and knowledge for safe, effective performance in the workplace.
Theoretically, if the system is correct and processes are followed by people who have the correct credentials, with quality assessment tools as a starting point, there is no reason to not achieve a quality end point.

The process of confirming what the quality starting point is, is to ensure that the assessment tools are fit-for-purpose, and to do that before the tools are used with students.
This is a “pre-use” activity and is known as pre-use validation.

Pre-use Validation
Pre-use validation is also known in the VET sector by names including:
- Assessment review
- Assessment health check
- Verification
- Pre-assessment validation
- Pre-implementation validation
In a pre-use validation activity, the assessment tools are reviewed to confirm that they cover all of the unit of competency evidence requirements, that they are fit-for-purpose with industry-relevant questions and tasks, clear instructions to users, and reliable benchmarks. This is done before the tools are given to students to use.
Pre-use validation typically consists of two activities:
- Validation of mapping
- Validation of the assessment tool

Validation of mapping
Firstly, a validation of mapping exercise is where the assessment mapping document, in conjunction with the assessor marking guide, is reviewed against the unit of competency to confirm:
- That the instruments have been written to collect enough of the right type of evidence
- The mapping data is correct. That is, that the mapping document is an accurate reflection of what is in the assessment tool and how its contents ‘map’ against, or cover, the unit
There is a specific skill set attached to confirming the validity of an assessment mapping document.
Common errors include not correctly identifying when a tool contains insufficient and/or invalid assessment tasks, or not identifying when data on the mapping document is incorrectly mapped. Both of these elements go directly toward whether or not the tool meets the unit requirements.
The process of validation of mapping is described in the performance evidence requirements of the unit of competency TAEASS413 Participate in assessment validation:
“… the individual must: use mapping documentation to evaluate whether the assessment tools cover all aspects of the [3 nationally recognised] units of competency and their assessment requirements…”

Meeting requirements of 1.3.2a
Validation of mapping can be done on its own to satisfy requirements in Outcome Standard 1.3.2a, or it may be completed as part of validation of an assessment tool. Outcome Standard 1.3.2a states:
“…An NVR registered training organisation demonstrates: the assessment is consistent with the requirements of the training product…”
Noting that the training product is the "AQF qualification, a skill set, a unit of competency, accredited short course or module."
A properly and accurately validated mapping document is one way to demonstrate that the assessment is consistent with what the unit of competency requires.

Validation of assessment tools
Secondly, a validation of assessment tool exercise is where the assessment tool and the template it is developed on are scrutinised to confirm the tool:
- Is fit-for-purpose
- Contains elements that increase its usability, including clear instructions for users
- Is relevant to the cohort and delivery methodology
- Incorporates suitable methods for evidence collection
- Aligns to the principles of assessment
- Can support assessment decisions made according to the rules of evidence
A validation of mapping may be performed at the same time to confirm the assessment tool meets all of the unit requirements.
Again, advanced analysis skills are required to determine the quality of the tool and how well it meets the points outlined above.

Meeting requirements of 1.3.2b
Validation of the assessment tool can be done on its own to satisfy requirements in Outcome Standard 1.3.2b, which states:
“…An NVR registered training organisation demonstrates: assessment tools are reviewed prior to use to ensure assessment can be conducted in a way that is consistent with the principles of assessment and rules of evidence set out under Standard 1.4…”
Standard 1.4 goes on to outline the:
Principles of assessment:
- Fairness
- Flexibility
- Validity
- Reliability
Rules of evidence:
- Validity
- Sufficiency
- Authenticity
- Currency
As part of the pre-use analysis of the assessment tool to satisfy 1.3.2b, a skilled validator will be looking to see whether the tool:
- Gives clear guidance to users on what, when, how and where assessment will occur
- Advises students on expectations and processes linked to assessment
- Considers individual student needs by embedding opportunity for reasonable adjustments and accommodations where needed (and allowable)
- Aims to collect valid evidence in a number of ways appropriate to the cohort and operational context
- Will allow the student the opportunity to have their skills and knowledge recognised no matter how they were acquired
- Embeds opportunity for students to demonstrate valid skills performance in industry-realistic settings
- Has benchmarks – including for expected observable behaviours and practical tasks – that guide assessment decision-making and mean any assessor can make consistent judgements across students and across time
- Allows for collection of evidence that will be:
- Sufficient and relevant to the requirements so that an assessor can decide whether the student has the skills and knowledge required for competency
- Done in a way that the assessor can confirm the evidence belongs to the student and is a product of what the student knows and can do
- Up-to-date with industry requirements for safe, effective workplace performance
In any cases where it is identified the tool does not include the necessary components for clear use or that it will not support any of the principles of assessment or rules of evidence, the tool must be edited to rectify the design shortfall/s before being put into the RTO’s assessment system and used with students.

Trialling, panelling and piloting
Trialling, panelling and piloting are terms that are not included or referenced in the Outcome Standards.
However, your RTO may decide to use one or more of these methods as how it demonstrates meeting the requirements linked to Outcome Standard 1.3.

Trialling
Trialling is a process of testing the tools before they are formally used with students. It allows an opportunity to see whether what’s on paper translates well into practice and for any refinements to be made. Trialling may involve trainers/assessors, willing students, and/or industry representatives. As explained in TAEASS512 Design and develop assessment tools, trialling is a part of finalising the development of the tool.

Panelling
Panelling is a process where the tools are reviewed by a panel of trainers/assessors with expertise in the unit/s of competency the assessment relates to and/or in assessment tool development. Again, this is a process of reviewing tools before they are formally used with students.

Piloting
Piloting is a process whereby an assessment tool is used with a small group of students who are representative of the intended cohort. Piloting allows a determination of whether the tool can be used effectively with a ‘real’ audience before widespread use with students. Any changes necessary as a result of the pilot are easier to manage with a reduced group of involved students.

Industry feedback
Getting industry feedback on your assessment tools is a sound method to confirm that the assessment will be relevant to, and representative of, skills and knowledge of current safe workplace practices.
However, it is unrealistic to expect subject matter experts to have intimate knowledge of the principles of assessment and rules of evidence – this is squarely in the domain of VET expertise.
Therefore, for the purposes of Outcome Standard 1.3.2b, be wary of assuming industry feedback on assessment tools will give assurances of meeting this requirement.
Industry feedback to ensure training reflects current industry practice is a requirement of Outcome Standard 1.2.

Credentials required for pre-use validation
While neither the Outcome Standards nor Credential Policy specify credentials required to undertake pre-use validation of assessment tools, it is recommended that the individual carrying out the activity has expert knowledge of assessment and advanced understanding of validity. Both TAE units of competency referenced in-text above refer to requirements for an individual to complete the activity.

Continuous improvement
Given the purpose of pre-use validation is to ensure assessment tools are covering all of the unit requirements and will be fit-for-use, where any deficits are identified, the materials should be edited to rectify the issues and then reviewed again to confirm validity.

Meeting requirements of 1.3.2c
The records of outcomes of the pre-use review activities may be in the form of a formal summary report, notes to the developer, and/or documents marked up with comments for review and action. The action taken based on these records can be used to satisfy requirements in Outcome Standard 1.3.2c, which states:
“…An NVR registered training organisation demonstrates: the outcomes of any such reviews inform any necessary changes to assessment tools …”

As a quality assurance process, when pre-use validation occurs, the review and analysis activities are completed before the assessment tools are used, and the RTO confirms requirements can be fulfilled.
|
Important note: the Outcome Standards are not prescriptive so they do not stipulate what an RTO must do to arrive at the necessary outcome. Your RTO may have a different way to confirm it has met requirements in 1.3. As long as it is a robust method that can be justified as producing accurate results, the RTO can use it. In this article, we have presented a logical option that takes into account the official definitions of various components and processes, is supported by established requirements in the Training and Education (TAE) Training Package, and conforms to the requirements stepped out in the Outcome Standards. |

Validation of assessment practices and judgements
The second reference to validation activity and by explicit use of the word ‘validation’ comes at Outcome Standard 1.5.
Here, it is expected that:
“…The assessment system is quality assured by appropriately skilled and credentialled persons through a regular process of validating assessment practices and judgements…”
This type of validation activity occurs after the assessment tools have been used with students, and judgements been made by assessors on the evidence produced as part of the assessment process.
Previous Standards also mandated the confirmation of assessment practices and judgements and RTOs have been used to sampling results for analysis and review.
In the VET sector, this type of validation has also been known by names including:
- Formal validation
- Post-use validation
- Post-implementation validation
- Validation of assessment judgements
Irrespective of the name, the aim of this type of validation activity is to confirm that the RTO's assessment system did consistently produce valid assessment judgments.
This validation is conducted after assessment is complete and students have been notified of their results - hence post-use validation.
Within a post-use validation process, validators are to consider the validity of both assessment practices and assessment judgements (how the assessment has been conducted/the assessment system used, and how the assessments have been marked). It is the latter which can be confused with moderation.
 Moderation
Moderation
Moderation is another activity that occurs post-use. Essentially a quality control process, moderation is a process of comparing judgments and confirming that across the board, and over time, assessors are giving similar results for similar evidence.
Moderation is completed after assessment evidence has been marked but before students are advised of their results. It aims to ensure all results decisions for a unit are aligned.

Requirements of Outcome Standard 1.5.2
Outcome Standard 1.5.2 steps out that the RTO must demonstrate:
a) They validate assessment practices and judgements to confirm competency decisions are in line with competency and compliance requirements
b) A rolling schedule ensures every training product on the RTO’s scope of registration is validated at least once every five years – and more frequently when higher risks present
c) That a risk-based approach informs the plan of what the RTO will validate, when
d) If the RTO delivers TAE qualifications or skill sets that enable assessment decisions to be made, independent validation of their system occurs once the first cohort of students have completed their training and assessment
e) Only people with relevant industry competency, industry currency and the specified credential for validation are involved in validation (the Credential Policy stipulates the credentials required)
f) Validation outcomes are not determined solely by the person who also wrote the materials and/or delivered the training and/or assessment
g) How the outcomes from validation of the system and tools that were used are then used to make required changes and improvements
Outcome Standard 1.5.2a requires that the review of assessment practices and judgements occurs after the tools have been used. Therefore, this is the post-use validation activity that seeks to confirm the quality end point:

As a quality review process, when validation of the assessment system occurs post-use the review and analysis activities are completed after the assessment tools are used, and the RTO confirms judgements were consistent, compliant and that requirements have been fulfilled.
The quality cycle diagram below shows the interdependence of quality outcomes on quality inputs throughout the assessment cycle:

Pre-use Validation - Validation of Mapping
Purpose of a Mapping Document
Before we look at validating the mapping document, let's have a very quick refresh on the purpose of the mapping document.
A mapping document is developed to go with the assessment.
It is used to:
- Plot and record coverage of an assessment against the unit of competency
- Record exactly which parts of an assessment can be attributed as gathering evidence for which unit requirements
- Set the foundation for good validation outcomes
Importance of Mapping
Done correctly, mapping ensures proper coverage of unit requirements and that assessment tools meet the Training Package requirements
- Outcome Standard 1.3.1 requires that the assessment system is ... consistent with the training product
The Role of Mapping in Compliance
Make it easy for someone looking for evidence that the assessment tool will do as it should
Use mapping to demonstrate compliance
- It's more than just having a mapping document
- The mapping must be valid too! It should be accurate
- Accurate mapping is a skill
For help on developing this skill, see the PD session ready to watch now: Assessment Mapping Do's and Don'ts
Purpose of Validating a Mapping Document
Before we even get into analysing whether an assessment tool has instructions to users, contains elements to address the Principles of Assessment etc., we need to ensure it will collect the evidence required for competency.
Given the mapping document is a way of saying "here's how this assessment tool is covering the unit of competency", it makes sense that this should be confirmed. Remember that in the context of general use, 'to validate' something means to check, prove or confirm that thing is true and/or correct.
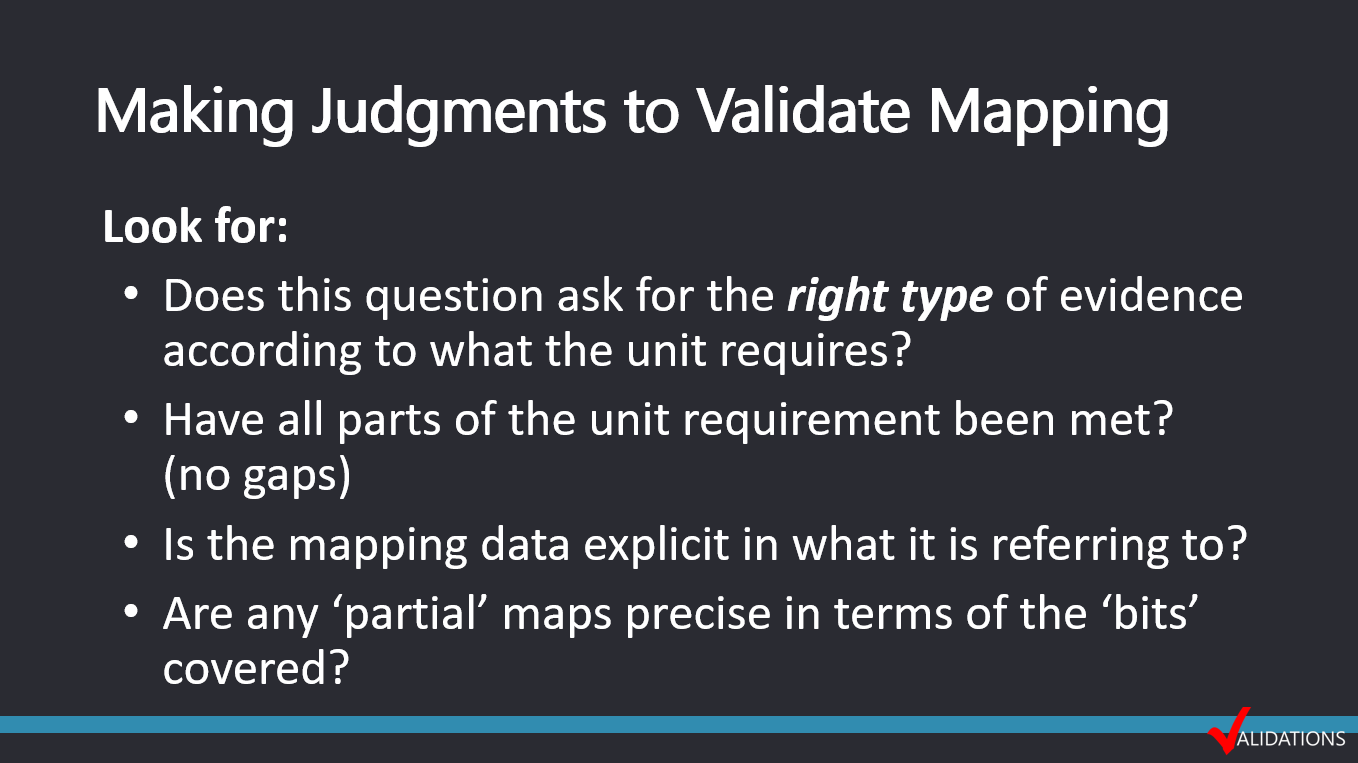
A validation of mapping is to verify:
- The unit of competency is covered (no gaps)
- Assessment questions/tasks are collecting the right type of evidence
- Accuracy of existing mapping

If you're an Education Matters annual subscriber, click through to see a video example of a validation of mapping activity.
(Exclusive content for subscribers - you must be signed in and part of Education Matters with a current annual membership subscription to view).
Note in response to multiple instances of plagiarism. Our work obviously resonates with people as we have noted multiple other sites using our wording and ideas.
The content on this page is original work by MAE Projects Pty Ltd and is copyright 2018 - 2025. Do not copy, rework or have AI summarise this information to display on your own website or information channel without permission and correct attribution
To cite this:
Validations (2025). About Validation. Accessed: https://www.skillseducation.com.au/pages/validation, dd.mm.yy
